The history of credit scoring in the United States dates back to the late 19th century when merchants started using “local credit bureaus” to share information about customers who didn’t pay their bills. The credit bureau would collect information on people’s payment histories and provide it to other merchants, who could then use that information to decide whether to extend credit.
In the 1950s, credit bureaus began using computers to store and analyze credit information, which made the process more efficient and accurate. In 1956, the Fair Isaac Corporation (now known as FICO) introduced the first credit scoring system, which used a statistical algorithm to predict a borrower’s likelihood of defaulting on a loan. This system quickly became the industry standard and is still widely used today.
Credit scores can also affect other areas of life, such as the ability to rent an apartment or get a job. Many landlords and employers use credit scores to evaluate potential tenants or employees, and a poor credit score can limit opportunities in these areas.
One of the primary ways that credit scores affect people’s ability to build wealth is through access to credit. With a good credit score, individuals may be able to qualify for low-interest loans, credit cards, and other forms of credit, which can provide the capital needed to invest in real estate, start a business, or make other investments. By using credit to invest in appreciating assets, individuals can build wealth over time, creating financial security and stability for themselves and their families; but what is a credit score and what are its benefits, how should it be used to create wealth, these questions will be broken down as follows:
What is the credit score?
A credit score is a numerical expression based on a statistical analysis of a person’s credit files, to represent the creditworthiness of that person. A credit score is primarily based on credit report information, typically sourced from credit bureaus.
Credit score in United States
In the United States, a credit score is a numerical representation of an individual’s creditworthiness. Credit bureaus, such as Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion, collect and maintain information about an individual’s credit history, including payment history, outstanding debt, length of credit history, and new credit inquiries.
Based on this information, credit bureaus use various algorithms to calculate a credit score, which typically ranges from 300 to 850. A higher credit score generally indicates that an individual is more likely to repay their debts, while a lower credit score indicates a higher risk of default.
Lenders, such as banks and credit card companies, use credit scores to evaluate an individual’s creditworthiness and decide whether to approve a loan or credit application. A good credit score can make it easier to get approved for loans, credit cards, and other financial products, as well as qualify for more favorable interest rates and terms. Conversely, a poor credit score can make it harder to get approved for credit, and may result in higher interest rates and less favorable loan terms.
How Credit Scores Are Calculated?
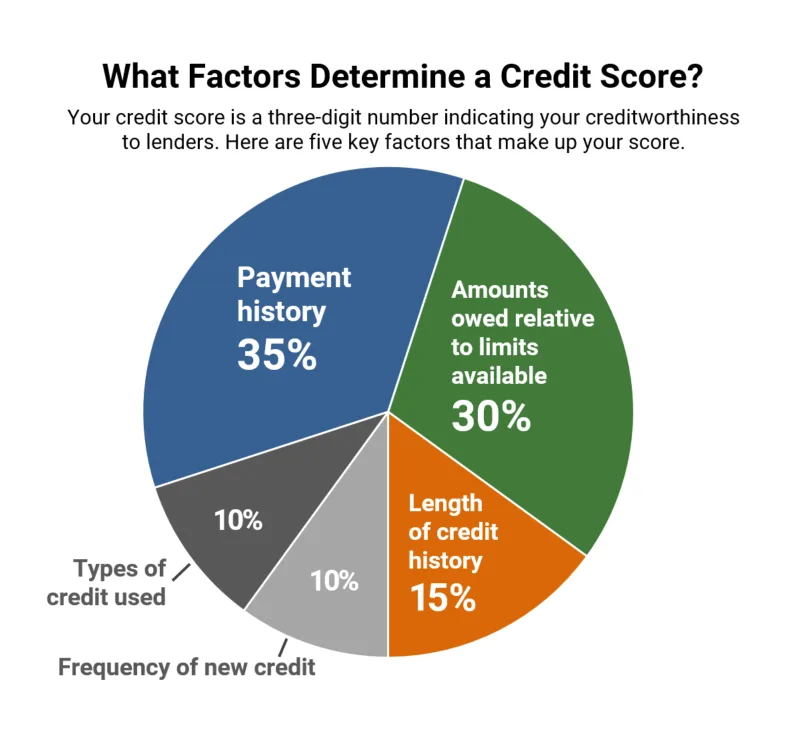
Credit scores are calculated using complex algorithms that take into account a wide range of factors related to your credit history. The specific formula used to calculate credit scores varies depending on the credit bureau and the credit scoring model being used, but here are some general factors that are typically considered:
Payment history: Your payment history is one of the most important factors in determining your credit score. Late or missed payments can have a significant negative impact on your score.
Credit utilization: Your credit utilization ratio is the amount of credit you’re using compared to your total credit limit. High credit utilization can indicate that you’re overextended and may be a higher risk for lenders.
Length of credit history: The length of your credit history is another important factor in determining your credit score. A longer credit history generally indicates that you’re a more experienced borrower and can be a positive factor in your score.
Types of credit: Having a mix of different types of credit (e.g., credit cards, auto loans, mortgages) can be a positive factor in your score.
New credit: Opening several new credit accounts in a short period of time can be a negative factor in your score, as it may indicate that you’re taking on too much debt.
Relationship between credit score and wealth building
There is a strong relationship between credit score and wealth building in the United States. This is because a good credit score is often necessary to access the credit and financing needed to build wealth over time.
For example, individuals with good credit scores are more likely to be approved for mortgages with favorable terms, which can enable them to purchase a home and build equity over time. They are also more likely to be approved for business loans and lines of credit, which can help them start or grow a business and create wealth.
On the other hand, individuals with poor credit scores may struggle to access credit and financing, which can make it difficult to build wealth. They may have a harder time obtaining mortgages, business loans, and other forms of credit, or may be subject to higher interest rates and less favorable loan terms. This can limit their ability to purchase assets, invest in their education or businesses, or take advantage of other opportunities for wealth building.
Can you build wealth even with a low or no credit score?
Yes, it is possible to build wealth even with a low or no credit score, but it may be more challenging. Without a good credit score, it may be more difficult to access credit and financing, which can limit your ability to invest, start a business, or purchase assets that appreciate in value. However, there are still strategies you can use to build wealth, even if you have a low or no credit score.
While a good credit score can make it easier to access credit and financing, it is not the only path to building wealth. By focusing on saving, investing, and building your skills and knowledge, you can still achieve financial success even without a high credit score.
Benefits of having a high credit score
Having a high credit score can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Access to better credit products: A high credit score can help you qualify for better credit products, such as low-interest credit cards, personal loans, and mortgages, which can save you money in interest payments.
- Lower interest rates: A high credit score can also help you secure lower interest rates on loans and credit cards, which can save you money in the long run and help you pay off debt faster.
- Higher credit limits: With a high credit score, you may be eligible for higher credit limits, which can provide more financial flexibility and allow you to make larger purchases or investments.
- Easier approval for rental applications: Some landlords and property managers may check your credit score as part of the rental application process. A high credit score can help you get approved for rental properties more easily, and may even result in lower security deposits.
- Better car insurance rates: Some car insurance companies use credit scores as a factor in setting insurance rates. With a high credit score, you may be eligible for lower car insurance rates, which can save you money on your monthly premiums.
- More negotiating power: With a high credit score, you may have more negotiating power when it comes to loan terms and interest rates. You can use your high credit score as leverage to negotiate more favorable loan terms or interest rates.
- Increased financial opportunities: With a high credit score, you may have access to more financial opportunities, such as credit cards with rewards programs or exclusive benefits, which can help you save money and earn rewards over time.
How the credit score should be used to create wealth
Using your credit score to create wealth involves using credit wisely to invest in appreciating assets that can increase your net worth over time. Here are some ways that you can use your credit score to create wealth:
Invest in real estate: Real estate can be a valuable asset that appreciates in value over time. With a good credit score, you may be able to qualify for a low-interest mortgage to purchase a home or rental property. By making timely mortgage payments, you can build equity in the property over time, which can increase your net worth.
Start a business: Starting a business can be a way to build wealth and achieve financial independence. With a good credit score, you may be able to qualify for a business loan or line of credit to finance your business venture. By using credit to invest in your business, you can increase your chances of success and create wealth over time.
Invest in stocks and other assets: With a good credit score, you may be able to qualify for a low-interest margin account or other forms of credit to invest in stocks, bonds, and other assets. By investing in a diversified portfolio of assets, you can potentially earn a higher rate of return and increase your net worth over time.
Consolidate high-interest debt: If you have high-interest credit card debt, consolidating it into a lower-interest loan can help you save money on interest and pay off the debt faster. With a good credit score, you may be able to qualify for a low-interest personal loan or balance transfer credit card to consolidate your debt and reduce your interest payments.
Use credit wisely: To use your credit score to create wealth, it’s important to use credit wisely and make timely payments on your debts. By paying your bills on time and keeping your credit utilization low, you can maintain a good credit score and qualify for favorable terms on loans and credit products, which can save you money in interest payments and help you build wealth over time.
How do I check my credit score?
There are several ways to check your credit score:
AnnualCreditReport.com: You can get a free credit report from each of the three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) once a year through AnnualCreditReport.com. While this report does not include your credit score, it does include detailed information about your credit accounts and payment history, which can help you understand your creditworthiness.
Credit card issuers: Many credit card issuers now offer free credit scores to their customers as a perk of using their card. You can usually access your credit score through your online account or mobile app.
Credit monitoring services: There are several credit monitoring services that provide access to your credit score, including Credit Karma, Credit Sesame, and Mint. These services typically provide regular updates on your credit score and offer tools and resources to help you improve your credit.
FICO Score Open Access program: Some lenders participate in the FICO Score Open Access program, which allows consumers to access their FICO score for free. You can check if your lender participates in this program and if they offer this benefit to their customers.
It’s important to note that there are different types of credit scores, and the score you receive may vary depending on the source you use. However, checking your credit score regularly can help you monitor your creditworthiness and identify any errors or fraudulent activity on your credit report.
What Do Your Credit Scores Mean?
Credit scores indicate how likely you are to repay borrowed money based on your credit history. A higher score suggests responsible credit use, making you more likely to qualify for loans and credit cards with favorable terms. On the other hand, lower scores indicate higher risk to lenders, potentially limiting your access to credit or leading to higher interest rates. Your score reflects your financial behavior, including payment history, credit utilization and length of credit history.

Exceptional: 800 to 850. FICO Scores ranging from 800 to 850 are considered exceptional. People with scores in this range typically experience easy approval processes when applying for new credit, and they are likely to be offered the best available lending terms, including the lowest interest rates and fees.
Very good: 740 to 799. FICO Scores in the 740 to 799 range are deemed very good. Individuals with scores in this range may qualify for better interest rates from lenders.
Good: 670 to 739. FICO Scores in the range of 670 to 739 are rated good. This range includes the average U.S. credit score, and lenders view consumers with scores in this range as “acceptable” borrowers. People with scores in this range are likely to qualify for a broad array of loans and credit cards, but are likely to be charged interest rates somewhat higher than the best available.
Fair: 580 to 669. FICO Scores that range from 580 to 669 are considered fair. Lenders may disqualify individuals with these scores if they apply for mainstream loans. Consumers with scores in this range may be considered subprime borrowers, eligible only for loans with interest rates significantly higher than the best available.
Poor: 300 to 579. FICO Scores that range from 300 to 579 are considered poor. Many lenders decline credit applications from people with scores in this range, which could be a result of bankruptcy or other major credit problems. Credit card applicants with scores in this range may only qualify for secured cards that require placing a cash deposit equal to the card’s spending limit. Utilities may require customers with scores in this range to put down sizable security deposits.
Is there a mobile app where I can regularly check my credit?

Yes, there are several mobile apps that you can use to regularly check your credit score and monitor your credit report. Here are some popular options:
Credit Karma: Credit Karma is a free app that provides access to your TransUnion and Equifax credit scores and credit reports. It also offers credit monitoring and personalized recommendations for improving your credit.
Credit Sesame: Credit Sesame is another free app that provides access to your TransUnion credit score and credit report. It also offers credit monitoring and personalized tips for improving your credit.
Mint: Mint is a personal finance app that offers a range of features, including access to your credit score and credit report. It also offers budgeting tools and investment tracking.
Experian: Experian is one of the major credit bureaus and offers a free app that provides access to your Experian credit score and credit report. It also offers credit monitoring and alerts for changes to your credit report.
myFICO: myFICO is a paid service that provides access to your FICO credit scores from all three major credit bureaus. It also offers credit monitoring and identity theft protection.
These apps can be a convenient way to monitor your credit and stay on top of any changes to your credit score or credit report.
Using Your Credit Score Wisely Can Help You Build and Accumulate Wealth
Your credit score is an important factor in your financial well-being. By using your credit score wisely, you can take advantage of opportunities to build and accumulate wealth.
One way to use your credit score to your advantage is to get better interest rates on loans. A higher credit score can help you qualify for lower interest rates on loans, such as mortgages, auto loans, and personal loans. By paying less in interest, you can save money over the life of the loan and use those savings to invest in other areas of your financial life.
Another way to use your credit score to build wealth is to take advantage of credit card rewards. Many credit cards offer cash back, points, or miles for every dollar you spend. By using your credit card wisely and paying off your balance in full each month, you can earn rewards without accruing interest charges or other fees.
FAQs
A credit score is a numerical expression based on an analysis of a person’s credit files, indicating their creditworthiness to lenders.
Credit scores in the U.S. are calculated using information from credit bureaus like Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion, considering factors such as payment history, debt, length of credit history, and new credit inquiries.
A good credit score can ease access to loans, credit cards, and favorable interest rates, enabling investments in real estate, businesses, and other wealth-building opportunities.
Key factors include payment history, credit utilization ratio, length of credit history, types of credit used, and recent credit inquiries.
Yes, landlords and employers often use credit scores to assess tenants and job applicants, potentially affecting rental approvals and job prospects.
You can check your credit score through AnnualCreditReport.com, credit card issuers, credit monitoring services like Credit Karma or Experian, or via lenders participating in the FICO Score Open Access program.
Credit score ranges (e.g., 300-850) indicate creditworthiness levels: exceptional (800-850), very good (740-799), good (670-739), fair (580-669), and poor (300-579).
A good credit score facilitates access to low-interest loans for real estate, business ventures, and investments, crucial for long-term wealth accumulation.
Yes, although more challenging, wealth-building is possible through savings, investments, and skill-building even with a low or no credit score.
Wisely use credit for investments like real estate, businesses, and stocks, and maintain good credit habits to secure favorable loan terms and opportunities.